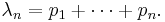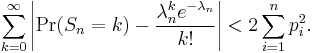Le Cam's theorem
In probability theory, Le Cam's theorem, named after Lucien le Cam (1924 – 2000), is as follows.
Suppose:
- X1, ..., Xn are independent random variables, each with a Bernoulli distribution (i.e., equal to either 0 or 1), not necessarily identically distributed.
- Pr(Xi = 1) = pi for i = 1, 2, 3, ...
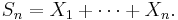 (i.e.
(i.e. 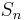 follows a Poisson binomial distribution)
follows a Poisson binomial distribution)
Then
In other words, the sum has approximately a Poisson distribution.
By setting pi = 2λn2/n, we see that this generalizes the usual Poisson limit theorem.
References
- Le Cam, L. (1960). "An Approximation Theorem for the Poisson Binomial Distribution". Pacific Journal of Mathematics 10 (4): 1181–1197. MR0142174. Zbl 0118.33601. http://projecteuclid.org/euclid.pjm/1103038058. Retrieved 2009-05-13.
- Le Cam, L. (1963). "On the Distribution of Sums of Independent Random Variables". Bernoulli, Bayes, Laplace: Proceedings of an International Research Seminar. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 179–202. MR0199871.
- Steele, J. M. (1994). "Le Cam's Inequality and Poisson Approximations". The American Mathematical Monthly 101 (1): 48–54. doi:10.2307/2325124. JSTOR 2325124.